In a world where data Information in analog or digital form that can be transmitted or processed. Read Full Definition is the new gold, how safe is your digital treasure? Every day, we share vast amounts of personal information online, but have you ever wondered what happens to it once it leaves your device? Enter the fascinating realm of cryptography – the art and science of keeping secrets safe in plain sight.
Information in analog or digital form that can be transmitted or processed. Read Full Definition is the new gold, how safe is your digital treasure? Every day, we share vast amounts of personal information online, but have you ever wondered what happens to it once it leaves your device? Enter the fascinating realm of cryptography – the art and science of keeping secrets safe in plain sight.
- Defining cryptography and its importance
- Historical evolution of cryptographic methods
- Classical Cryptography (Ancient times – 19th century):
- Mechanical Cryptography (19th century – Mid-20th century):
- Modern Cryptography (Mid-20th century – Present):
- Key principles of modern cryptography
- Basic Terminologies
- Types of Cryptography Encryption Techniques: Safeguarding Your Data
- Symmetric Key Cryptography: Speed and efficiency
- Asymmetric Key Cryptography: Enhanced security
- Hash Functions (Hashing): Ensuring data integrity
- Digital signatures: Authenticity and non-repudiation
- Real-World Applications of Cryptography
- A. Secure communication in messaging apps
- B. Protecting financial transactions
- C. Safeguarding sensitive government information
- D. Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies
- Conclusion
- FAQs:
From ancient ciphers to cutting-edge algorithms, cryptography has been the silent guardian of our most valuable information for centuries. But in today’s digital age, its importance has skyrocketed. Whether you’re sending a confidential email, making an online purchase, or browsing the web, cryptography works tirelessly behind the scenes to protect your data.
In this blog post, we’ll unlock the secrets of cryptography, exploring its fundamental concepts, powerful encryptionEncryption is the process in which the message or data is scrambled using the various algorithms available in all cryptographic algorithms. Read Full Definition techniques, and real-world applications. We’ll also delve into the thrilling world of cryptanalysis and discover how you can implement cryptographic principles in your daily life. Ready to crack the code? Let’s dive in!
Defining cryptography and its importance
Cryptography, at its core, is the art and science of secure communication in the presence of adversaries. It’s a fundamental pillar of modern information security, serving as the bedrock for protecting sensitive data in our increasingly digital world. The term “cryptography” originates from the Greek words “kryptos,” meaning hidden, and “graphein,” meaning to write. This etymology perfectly encapsulates the essence of cryptography: the practice of concealing information from unauthorized parties.
Cryptography is an invaluable tool widely used worldwide to encrypt data and information, making data hiding possible. Cryptography is a complex science that converts plaintext into ciphertext and involves various methods for sending messages in a hidden form, so that only authorized recipients can decipher the disguise and read the message.
The primary purpose of cryptography is to ensure that the data is secure and cannot be accessed by unauthorized individuals. In today’s interconnected digital landscape, the importance of cryptography cannot be overstated. It plays a crucial role in safeguarding various aspects of our daily lives, from secure online transactions to protecting national security. Here are some key reasons why cryptography is vital in the modern world:
- Data Privacy: Cryptography ensures that sensitive information remains confidential, protecting personal and corporate data from unauthorized access.
- Data Integrity: It verifies that data has not been tampered with during transmission or storage, maintaining the accuracyIn scientific and measurement contexts, "accuracy" refers to the degree of proximity or closeness between a measured value and the true or actual value of the measured quantity. Accuracy indicates how well a measurement reflects Read Full Definition and consistency of the information.
- AuthenticationVerifying the identity of a user, process, or device, often as a prerequisite to allowing access to resources in an information system. Read Full Definition: Cryptographic techniques allow us to confirm the identity of individuals or systems, preventing impersonation and unauthorized access.
- Non-repudiation: This aspect of cryptography ensures that a party cannot deny the authenticity of their signature on a document or the sending of a message.
- Secure Communication: Cryptography enables secure communication over insecure channels, such as the internet, by encrypting messages.
To better understand the multifaceted importance of cryptography, let’s look at a comparison of scenarios with and without cryptographic protection:
| Scenario | Without Cryptography | With Cryptography |
|---|---|---|
| Online Banking | Vulnerable to eavesdropping and data theft | Secure transactions, protected account information |
| Email Communication | Messages can be intercepted and read | End-to-end encryption ensures message privacy |
| Password Storage | Stored in plain text, easily compromised | Hashed and salted, resistant to breaches |
| File Storage | Sensitive documents at risk of unauthorized access | Encrypted files remain secure even if physically accessed |
| Digital Signatures | Easily forged or tampered with | Provides authenticity and non-repudiation |
As we delve deeper into the world of cryptography, it’s essential to recognize its pervasive influence on our digital lives. From the moment we unlock our smartphones to the complex algorithms protecting global financial systems, cryptography works tirelessly behind the scenes to ensure our digital world remains secure.
Historical evolution of cryptographic methods
The journey of cryptography through history is a fascinating tale of human ingenuity, evolving alongside technological advancements and the ever-growing need for secure communication. This evolution can be broadly categorized into three main eras: classical cryptography, mechanical cryptography, and modern cryptography.
Classical Cryptography (Ancient times – 19th century):
The roots of cryptography can be traced back to ancient civilizations. Early methods were primarily focused on simple substitution and transposition ciphers. Here are some notable examples:
- Scytale (Ancient Greece, 7th century BCE): One of the earliest known cryptographic devices, it consisted of a cylinder with a strip of parchment wound around it. The message was written lengthwise and unwound to scramble it.
- Caesar Cipher (Roman Empire, 1st century BCE): Named after Julius Caesar, this substitution cipher involved shifting each letter in the plaintext by a fixed number of positions in the alphabet.
- Vigenère Cipher (16th century): An improvement over simple substitution ciphers, it used a keyword to shift letters in the plaintext, making it significantly harder to break.
These classical methods, while innovative for their time, were primarily based on the secrecy of the algorithm itself, a principle that modern cryptography has moved away from.
Mechanical Cryptography (19th century – Mid-20th century):
The industrial revolution brought about mechanical devices that could perform more complex encryption processes:
- Hebern Rotor Machine (1917): Created by Edward Hebern, this was one of the first electromechanical cipher machines, using a single rotor for encryption.
- Enigma Machine (1918-1945): Famously used by Nazi Germany during World War II, the Enigma machine used multiple rotors to create a polyalphabetic substitution cipher.
- SIGABA (1940s): Developed by the US, this machine was never successfully cryptanalyzed during its operational lifetime, a testament to its sophisticated design.
These mechanical devices significantly increased the complexity and security of encryption, but they were still vulnerable to dedicated cryptanalysis efforts.
Modern Cryptography (Mid-20th century – Present):
The advent of computers and digital technology ushered in a new era of cryptography, characterized by mathematical algorithms and computational security:
- DES (Data Encryption Standard, 1977): One of the first standardized symmetric-key algorithms, widely used until the late 1990s.
- RSA (1978): Named after its creators, Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman, this public-key cryptosystem revolutionized secure communication and remains widely used today.
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard, 2001): The current standard for symmetric encryption, offering robust security for various applications.
- Elliptic Curve Cryptography (1985): Offering comparable security to RSA with shorter key lengths, ECC has gained popularity, especially in resource-constrained environments.
To illustrate the evolution of cryptographic methods, let’s compare their characteristics:
| Era | Method | Key Characteristic | Strength | Weakness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classical | Caesar Cipher | Letter substitution | Simple to implement | Easy to break with frequencyFrequency is a fundamental concept in physics and wave theory. It refers to the number of times a specific point on a wave, such as a crest or trough, passes a fixed reference point in Read Full Definition analysis |
| Mechanical | Enigma Machine | Rotor-based polyalphabetic substitution | Complex for its time | Vulnerable to dedicated cryptanalysis |
| Modern | AES | Block cipher with multiple rounds | Highly secure, efficient | Requires secure key management |
This historical journey highlights the constant cat-and-mouse game between cryptographers and cryptanalysts. As encryption methods became more sophisticated, so did the techniques to break them, driving continuous innovation in the field.
Key principles of modern cryptography

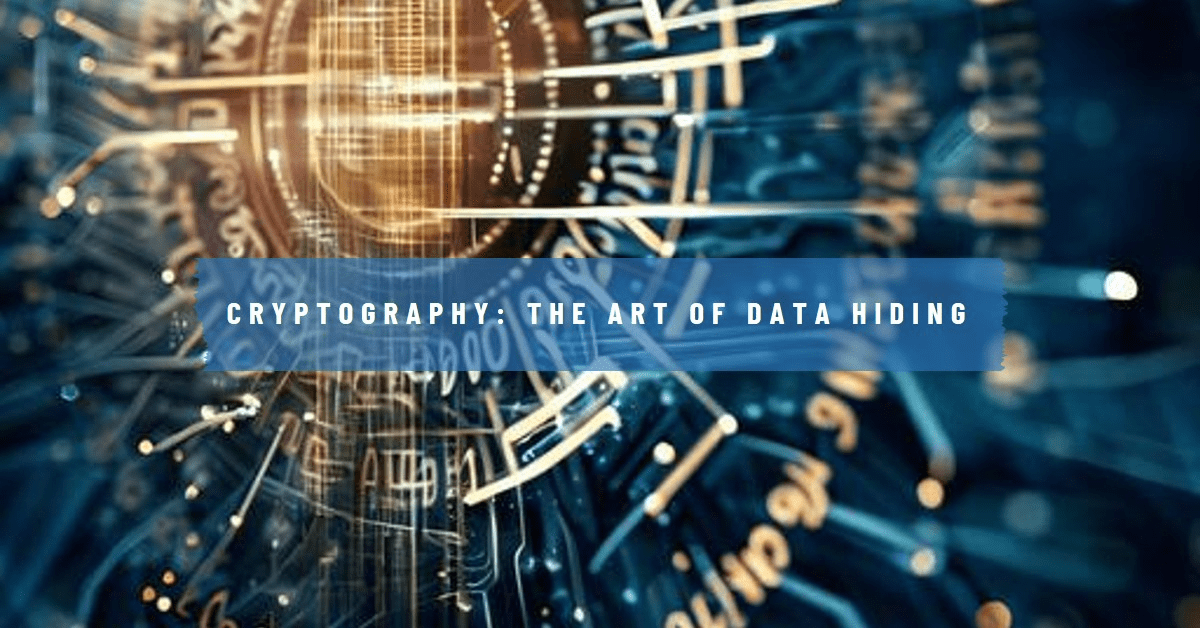
Modern cryptography is built upon a foundation of mathematical principles and rigorous security definitions. Unlike its historical counterparts, which relied on the secrecy of the algorithm, modern cryptography adheres to Kerckhoffs’s principle: a cryptosystem should be secure even if all aspects of the system, except the key, are public knowledge. This paradigm shift has led to the development of several key principles that form the cornerstone of contemporary cryptographic systems:
- Confidentiality: Ensures that information remains private and secret from unauthorized parties. It is typically achieved through encryption, which transforms plaintext into ciphertext using a secret key. Modern encryption algorithms, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), provide strong confidentiality guarantees.
- Integrity: This principle ensures that data has not been altered in an unauthorized manner since it was created, transmitted, or stored. Cryptographic hash functions and digital signatures play a crucial role in maintaining data integrity.
- Authentication: Authentication verifies the identity of the parties involved in a communication or transaction. It answers the question, “Are you who you claim to be?” Public key infrastructure (PKI) and digital certificates are commonly used for authentication in modern cryptographic systems.
- Non-repudiation: Non-repudiation prevents an individual or entity from denying that they performed a particular action. It’s crucial in scenarios like digital contracts or financial transactions. Digital signatures, based on public-key cryptography, provide non-repudiation.
- Key Management: The secure generation, storage, distribution, and destruction of cryptographic keys are vital to the overall security of a cryptosystem. Poor key management can undermine even the strongest encryption algorithms.
- Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS): PFS ensures that if a long-term key is compromised, it does not affect the security of past session keys. This principle is increasingly crucial in protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security).
- Computational Security: Modern cryptographic systems are designed to be computationally secure, meaning they are secure against adversaries with limited computational resources. Security often relies on the presumed difficulty of mathematical problems, such as integer factorization or the discrete logarithm problem.
- Randomness and Unpredictability: High-quality random number generation is crucial for many cryptographic operations, including key generation and creating initialization vectors. Cryptographically secure pseudo-random number generators (CSPRNGs) are used to ensure unpredictability.
- Resistance to Known Attacks: Modern cryptographic algorithms and protocols are designed to resist known types of attacks, such as chosen-plaintext attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, and side-channel attacks.
- Open Design: Following Kerckhoffs’s principle, modern cryptographic algorithms are publicly known and scrutinized by the global cryptography community. This open approach helps identify and fix vulnerabilities more effectively than relying on the secrecy of the algorithm.
To illustrate how these principles are applied in practice, let’s consider a standard cryptographic protocol: HTTPS (HTTP over Secure Sockets Layer). Here’s how it incorporates various cryptographic principles:
| Principle | Application in HTTPS |
|---|---|
| Confidentiality | Uses symmetric encryption (e.g., AES) for bulk data encryption |
| Integrity | Employs HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code) to ensure data hasn’t been tampered with |
| Authentication | Uses digital certificates to authenticate the server (and optionally the client) |
| Non-repudiation | Server’s digital signature on its certificate provides non-repudiation |
| Key Management | Uses key exchange protocols (e.g., Diffie-Hellman) for secure key establishment |
| Perfect Forward Secrecy | Implemented through ephemeral Diffie-Hellman key exchange |
| Computational Security | Based on well-studied mathematical problems (e.g., the discrete logarithm problem) |
| Randomness | Uses CSPRNGs for generating session keys and other random values |
| Resistance to Attacks | Designed to resist various attacks, including downgrade attacks and replay attacks |
| Open Design | TLS protocol specifications are publicly available and widely scrutinized |
These principles of modern cryptography work in concert to provide a robust framework for secure communication and data protection. They form the basis for numerous security protocols and applications that we rely on daily, including secure messaging apps, virtual private networks (VPNs), and blockchain technologies.
As we move forward, it’s crucial to understand that cryptography is an ever-evolving field. Emerging technologies, such as quantum computing, pose new challenges, prompting the development of post-quantum cryptography. Simultaneously, advancements in areas like homomorphic encryption and zero-knowledge proofs are opening up new possibilities for privacy-preserving computation and verification.
Basic Terminologies
Cryptography involves several basic terms that define various operations. These terms include cipher, ciphertext, decryptionDecryption is the process of converting the cipher text back to the original text to read the message. Read Full Definition, encryption, key, plaintext, and digital signature.
Overall, cryptography is a complex science that involves various methods and techniques to ensure data is secure and cannot be accessed by unauthorized individuals.
Types of Cryptography Encryption Techniques: Safeguarding Your Data
The three types of Cryptography include Symmetric Key Cryptography, Asymmetric Key Cryptography, and Hash Functions. Each type has advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of type depends on the specific use case.
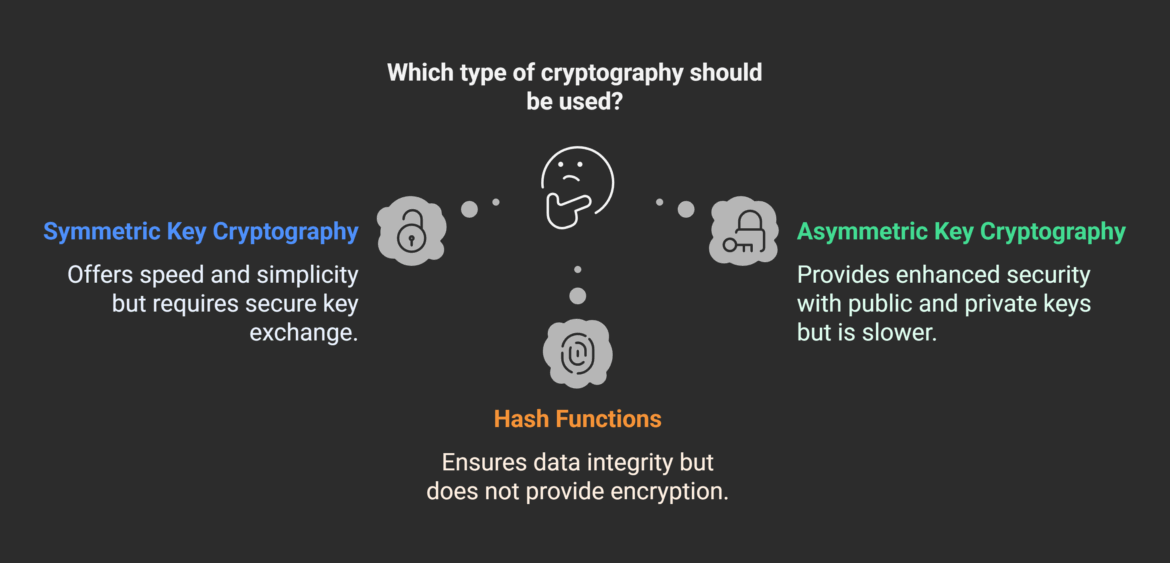
Symmetric Key Cryptography: Speed and efficiency
Symmetric Key Cryptography stands as a cornerstone in the realm of data protection, offering a blend of speed and efficiency that makes it indispensable in modern cryptography. This method, also known as secret-key cryptography, employs a single key for both encryption and decryption processes. Therefore, it is also known as Similar Key Cryptography. This type of cryptography is faster and less demanding compared to its asymmetric counterpart, but it requires a secure method of delivering keys.
At its core, symmetric encryption operates on a simple principle: the sender and receiver share a secret key. This key is used to scramble the original message (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext) and then decode it back to its original form. The strength of this method lies in its simplicity and speed, making it ideal for encrypting large volumes of data quickly.
Additionally, symmetric key cryptography only provides confidentiality, not authenticity or non-repudiation. Some famous examples of Symmetric Key Cryptography include the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), the Data Encryption Standard (DES), Triple DES (3DES), Blowfish, and Twofish. Despite its limitations, Symmetric Key Cryptography remains an essential tool for securing data, particularly in situations where speed is a priority and key distribution is not a concern.
Let’s delve deeper into the AES algorithm, as it’s currently the most popular and secure symmetric encryption method:
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
AES, developed by Belgian cryptographers Joan Daemen and Vincent Rijmen, was adopted by the U.S. government in 2001 as a replacement for the aging DES algorithm. It operates on blocks of data and supports key sizes of 128, 192, and 256 bits.
The AES encryption process involves several rounds of substitution and permutation operations, with the number of rounds depending on the key size:
- 128-bit key: 10 rounds
- 192-bit key: 12 rounds
- 256-bit key: 14 rounds
Each round consists of four main steps:
- SubBytes: Substitution of each byte using a lookup table
- ShiftRows: Shifting the rows of the state array
- MixColumns: Mixing the data within each column of the state array
- AddRoundKey: Adding the round key to the state
The decryption process follows the same steps in reverse order, using inverse operations.
The efficiency of symmetric encryption is evident in its performance. Here’s a comparison of encryption speeds for different key sizes of AES:
| Key Size | Encryption Speed (MB/s) | Relative Speed |
|---|---|---|
| 128-bit | 750 | 1.00x |
| 192-bit | 650 | 0.87x |
| 256-bit | 550 | 0.73x |
As we can see, even with the highest level of security (256-bit key), AES still maintains impressive speed, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
However, symmetric encryption is not without its challenges. The main drawback is key distribution – securely sharing the secret key between parties can be problematic, especially over long distances or insecure channels. This is where asymmetric encryption comes into play, which we’ll explore in the next section.
Asymmetric Key Cryptography: Enhanced security
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key cryptography, addresses the key distribution problem inherent in symmetric encryption while offering enhanced security features. This method uses a pair of keys that are different yet mathematically related: a public key and a private key.
The fundamental principle of asymmetric encryption is that data encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the corresponding private key, and vice versa. This elegant solution allows for secure communication without the need to share secret keys.
Key features of asymmetric encryption include:
- Enhanced security: The private key never needs to be shared, reducing the risk of compromise.
- Digital signatures: The ability to sign messages, ensuring authenticity and non-repudiation.
- Key exchange: Facilitates secure key exchange for symmetric encryption systems.
- Scalability: Easier to manage in large networks compared to symmetric encryption, making it a preferred method for secure communication over open networks such as the internet.
Additionally, Asymmetric Key Cryptography can provide authentication and non-repudiation, which means that the sender of the message cannot deny sending it and that the recipient can verify the message’s authenticity. However, it operates more slowly than symmetric systems and involves mathematically intensive tasks, making it more complex and challenging to implement.
Some popular asymmetric encryption algorithms include RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), Diffie-Hellman, ElGamal, and Digital Signature Standard (DSS). Despite its complexity, Asymmetric Key Cryptography has become an essential part of our digital life and is widely used to secure our online transactions, communication, and other sensitive information.
Let’s take a closer look at the widely used RSA algorithm:
RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
RSA, named after its inventors Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman, is based on the mathematical difficulty of factoring large numbers. The algorithm involves the following steps:
- Key generation:
- Choose two large prime numbers, p and q
- Compute n = p * q
- Calculate φ(n) = (p-1) * (q-1)
- Choose an integer e such that 1 < e < φ(n) and gcd(e, φ(n)) = 1
- Compute d such that d * e ≡ 1 (mod φ(n))
- Public key is (n, e), private key is (n, d)
- Encryption:
- Convert the message to a number m
- Compute ciphertext c = m^e mod n
- Decryption:
- Compute plaintext m = c^d mod n
The security of RSA relies on the computational infeasibility of factoring the product of two large prime numbers. As computing power increases, larger key sizes are needed to maintain security.
Here’s a comparison of RSA key sizes and their equivalent symmetric key strengths:
| RSA Key Size | Equivalent Symmetric Key Strength | Year of Equivalence |
|---|---|---|
| 1024-bit | 80-bit | 2010 |
| 2048-bit | 112-bit | 2030 |
| 3072-bit | 128-bit | 2040 |
| 7680-bit | 192-bit | 2080 |
| 15360-bit | 256-bit | 2120 |
While asymmetric encryption offers enhanced security, it comes at the cost of performance. Asymmetric algorithms are typically 1000-10000 times slower than symmetric algorithms. This is why in practice, asymmetric encryption is often used to securely exchange symmetric keys, which are then used for bulk data encryption.
Hash Functions (Hashing): Ensuring data integrity
Hash functions are a more advanced type of function compared to the ones mentioned earlier. They are designed to be more secure, but the tradeoff is that they can be slower and generate more data. This is because hash functions are designed so that even a small change in the input data results in a completely different hash value.
Hashing is a crucial component in the cryptographer’s toolkit, primarily used to ensure data integrity and create digital fingerprintsFingerprint, impression made by the papillary ridges on the ends of the fingers and thumbs. Fingerprints afford an infallible means of personal identification, because the ridge arrangement on every finger of every human being is Read Full Definition of data. Unlike encryption, hashing is a one-way process – it transforms input data of any size into a fixed-size output, called a hash or digest, which cannot be reversed to obtain the original data.
Key characteristics of hash functions include:
- Deterministic: The same input always produces the same hash.
- Quick computation: Hash values can be calculated rapidly for any given data.
- Pre-image resistance: It should be computationally infeasible to reconstruct the input data from its hash.
- Collision resistance: It should be extremely difficult to find two different inputs that produce the same hash.
- Avalanche effect: A small change in the input should result in a significantly different hash.
In cryptography, various hashing algorithms are used to ensure data security, with some of the most popular ones being MD5 (Message Digest algorithm 5), SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1), the SHA-2 family (SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512), SHA-3, and BLAKE2 and Whirlpool.
These algorithms generate a unique digital fingerprint for a given message or dataset, making it virtually impossible to reverse-engineer the original information. Using these algorithms, organizations can ensure that their data remains secure and that potential breaches are mitigated. Additionally, hash functions have become increasingly important in today’s digital age, where sensitive information is constantly being transmitted over the internet and stored on various devices.
Typical applications of hashing include:
- Password storage: Storing hashed passwords instead of plaintext. Operating systems typically use hash functions to store passwords because they effectively secure sensitive data.
- Data integrity checks: Verifying that data hasn’t been tampered with
- Digital signatures: Creating a digest of the message to be signed.
- Proof-of-work systems: Used in blockchain and cryptocurrency technologies
Let’s examine the SHA-256 algorithm, which is part of the SHA-2 family and widely used in various applications:
SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit)
SHA-256 produces a 256-bit (32-byte) hash value, typically rendered as a 64-digit hexadecimal number. The algorithm operates on 512-bit blocks and involves the following steps:
- Padding: The input message is padded to ensure its length is a multiple of 512 bits.
- Parsing: The padded message is parsed into 512-bit blocks.
- Setting initial hash values: Eight 32-bit words are initialized with the first 32 bits of the fractional parts of the square roots of the first 8 primes.
- Processing: Each 512-bit block undergoes 64 rounds of processing, involving bitwise operations, modular addition, and nonlinear functions.
- Final hash: The result of processing all blocks is combined to produce the final 256-bit hash value.
Here’s an example of SHA-256 in action:
Input: "Hello, World!"
SHA-256 Hash: A591A6D40BF420404A011733CFB7B190D62C65BF0BCDA32B57B277D9AD9F146ETo illustrate the avalanche effect, let’s change just one character:
Input: "Hello, World."
SHA-256 Hash: 68E656B251E67E8358BEF8483AB0D51C6619F3E7A1A9F0E75838D41FF368F728As we can see, a minor change in the input results in a completely different hash value.
Hash functions play a crucial role in various cryptographic protocols and applications. For instance, in blockchain technology, SHA-256 is used to create the “proof of work” that miners must solve to add new blocks to the chain.
Here’s a comparison of some popular hash functions:
| Hash Function | Output Size (bits) | Block Size (bits) | Collision Resistance | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 128 | 512 | Weak | Fast |
| SHA-1 | 160 | 512 | Weak | Fast |
| SHA-256 | 256 | 512 | Strong | Medium |
| SHA-3-256 | 256 | 1088 | Strong | Slow |
| BLAKE2b | 8-512 | 1024 | Strong | Very Fast |
While MD5 and SHA-1 are still used in some legacy systems, they are considered cryptographically broken and should be avoided for security-critical applications. SHA-256 and newer algorithms like SHA-3 and BLAKE2 are recommended for current and future use.
Digital signatures: Authenticity and non-repudiation
Digital signatures represent a powerful application of asymmetric cryptography, providing a means to ensure the authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation of digital messages or documents. They serve as the electronic equivalent of handwritten signatures or stamped seals, but with far greater security and verifiability.
The primary purposes of digital signatures are:
- Authentication: Verifying the identity of the sender
- Integrity: Ensuring the message hasn’t been altered in transit
- Non-repudiation: Preventing the sender from denying they sent the message
The process of creating and verifying a digital signature involves the following steps:
- The sender creates a hash of the message.
- The hash is encrypted using the sender’s private key, creating the digital signature.
- The signature is appended to the message and sent.
- The recipient decrypts the signature using the sender’s public key.
- The recipient independently hashes the received message.
- If the decrypted hash matches the independently computed hash, the signature is valid.
Popular digital signature algorithms include:
- RSA-PSS (Probabilistic Signature Scheme)
- DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm)
- ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm)
- EdDSA (Edwards-curve Digital Signature Algorithm)
Real-World Applications of Cryptography
A. Secure communication in messaging apps
In today’s digital age, secure communication has become crucial, especially in the messaging apps we use daily. Cryptography plays a crucial role in ensuring that our private conversations remain private. Let’s explore how cryptography is used in popular messaging apps to protect our data.
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is the cornerstone of secure messaging. This cryptographic technique ensures that only the sender and intended recipient can read the messages, preventing any third party, including the service provider, from accessing the content. Apps like WhatsApp, Signal, and Telegram have implemented end-to-end encryption (E2EE) to safeguard user privacy.
Here’s how E2EE works in messaging apps:
- Key generation: When you install the app, it generates a unique pair of cryptographic keys – a public key and a private key.
- Key exchange: Your public key is shared with your contacts, while your private key remains securely stored on your device.
- Message encryption: When you send a message, it’s encrypted using the recipient’s public key.
- Message decryption: The recipient’s device uses their private key to decrypt the message.
This process ensures that even if the messages are intercepted during transmission, they remain unreadable without the corresponding private key.
Let’s compare some popular messaging apps and their cryptographic features:
| App Name | End-to-End Encryption | Protocol Used | Additional Security Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (default) | Signal Protocol | Disappearing messages, Two-step verification | |
| Signal | Yes (default) | Signal Protocol | Self-destructing messages, Screen security |
| Telegram | Optional (Secret Chats) | MTProto | Self-destructing messages, Passcode lock |
| iMessage | Yes (default) | Apple’s proprietary protocol | Two-factor authentication |
While these apps provide strong encryption, it’s essential to understand that the security of your messages also depends on factors like device security and user behavior. Always keep your devices up to date and be cautious about sharing sensitive information with others.
B. Protecting financial transactions
Cryptography forms the backbone of secure financial transactions in our increasingly digital economy. From online banking to cryptocurrency exchanges, cryptographic techniques ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and authenticity of financial data.
One of the most critical applications of cryptography in finance is in securing online banking transactions. Here’s how cryptography protects your money when you bank online:
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) / Transport Layer Security (TLS): These protocols use public key cryptography to establish a secure connection between your device and the bank’s server.
- Digital signatures: These verify the authenticity of transactions and prevent unauthorized modifications.
- One-time passwords (OTP): These use cryptographic algorithms to generate unique, temporary codes for transaction authorization.
- Tokenization: This replaces sensitive data, such as credit card numbers, with unique identification symbols, maintaining data security while still allowing for its use in financial systems.
Cryptography also plays a vital role in protecting ATM transactions. When you insert your card and enter your PIN, several cryptographic processes occur:
- The PIN is encrypted before being sent to the bank for verification.
- The communication between the ATM and the bank is encrypted to prevent eavesdropping.
- The ATM uses cryptographic techniques to authenticate itself to the bank’s network, preventing fake ATMs from accessing the system.
In the realm of e-commerce, cryptography ensures secure online payments. Here’s a simplified overview of how a typical online transaction is secured:
- You enter your credit card details on a secure website (HTTPS).
- The website encrypts your data using the payment gateway’s public key.
- The encrypted data is sent to the payment gateway.
- The gateway decrypts the data using its private key and processes the payment.
- The result is encrypted and sent back to the merchant’s website.
This process ensures that your financial information remains confidential throughout the transaction.
Cryptography also underpins the security of mobile payment systems, such as Apple Pay and Google Pay. These systems use tokenization to replace your actual credit card number with a device-specific token. Even if this token is intercepted, it’s useless without the cryptographic keys stored in your device’s secure element.
C. Safeguarding sensitive government information
Governments around the world rely heavily on cryptography to protect classified information and maintain national security. The use of cryptography in government operations spans a range of areas, from secure communication channels to protecting critical infrastructure.
One of the primary applications of cryptography in government is in classified communications. Advanced encryption standards are used to secure:
- Diplomatic cables between embassies and foreign ministries
- Military communications on the battlefield
- Intelligence agency reports and communications
- Sensitive policy discussions among high-level officials
The encryption methods used for these purposes are often more advanced than those available commercially. Some governments have developed their own proprietary encryption algorithms.
Cryptography also plays a crucial role in protecting critical national infrastructure. This includes:
- Power grids
- Water supply systems
- Transportation networks
- Healthcare systems
- Financial institutions
These systems are increasingly interconnected and digitalized, making them potential targets for cyberattacks. Cryptography helps secure these systems by:
- Encrypting data transmitted between different components of the infrastructure
- Authenticating users and devices to prevent unauthorized access
- Ensuring the integrity of control signals and system updates
Another vital application of cryptography in government is in secure voting systems. As many countries move towards electronic voting, cryptography ensures:
- Voter privacy: Encrypting votes so they can’t be linked back to individual voters
- Vote integrity: Preventing votes from being altered after they’re cast
- Verifiability: Allowing voters to verify that their vote was correctly recorded without compromising the secrecy of their ballot
Here’s a simplified overview of how cryptography might be used in an electronic voting system:
| Stage | Cryptographic Technique | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Voter Registration | Digital signatures | Authenticate voters |
| Ballot Casting | Homomorphic encryption | Allow vote counting without decrypting individual votes |
| Vote Transmission | End-to-end encryption | Protect votes during transmission |
| Vote Counting | Zero-knowledge proofs | Prove the correctness of the count without revealing individual votes |
Governments also use cryptography to protect sensitive documents and databases. This includes:
- Citizen identity information
- Tax records
- Health records
- Criminal justice information
These databases are encrypted to prevent unauthorized access, and cryptographic access controls ensure that only authorized personnel can view or modify the data.
Lastly, cryptography plays a crucial role in government-to-government communication, particularly in areas such as intelligence sharing and diplomatic negotiations. Secure communication channels, often using quantum key distribution for maximum security, ensure that sensitive international discussions remain confidential.
D. Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies
Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies are among the most innovative and disruptive applications of cryptography in recent years. These technologies leverage various cryptographic techniques to create decentralized, secure, and transparent systems for storing and transferring value.
At its core, a blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Each ‘block’ in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating an immutable chain of records. This structure, combined with consensus mechanisms, makes blockchains extremely resistant to tampering and fraud.
Here are some key cryptographic elements used in blockchain technology:
- Hash functions: These one-way functions convert input data of any size into a fixed-size output. In blockchains, hash functions are used to:
- Create unique identifiers for blocks
- Link blocks together in the chain
- Generate proof-of-work in mining processes
- Public key cryptography: This is used to create digital wallets and sign transactions. Each user has a pair of keys:
- A public key, which serves as the wallet address
- A private key, used to sign transactions and prove ownership of funds
- Digital signatures: These verify the authenticity of transactions and ensure that only the rightful owner can spend their funds.
- Merkle trees: These data structures efficiently summarize all the transactions in a block, allowing for quick verification of large datasets.
Now, let’s look at how these cryptographic elements come together in a typical cryptocurrency transaction:
- Alice wants to send Bitcoin to Bob.
- Alice creates a transaction, specifying Bob’s public key as the recipient.
- Alice signs the transaction with her private key.
- The transaction is broadcast to the network.
- Miners verify the transaction using Alice’s public key and include it in a block.
- The block is added to the blockchain after solving a cryptographic puzzle, known as proof of work.
- Bob can now spend the received Bitcoin using his private key.
This process ensures that transactions are secure, irreversible, and resistant to double-spending.
While Bitcoin was the first and remains the most well-known application of blockchain technology, numerous other cryptocurrencies and blockchain platforms have emerged, each with its own cryptographic innovations:
| Platform | Key Cryptographic Features |
|---|---|
| Ethereum | Smart contracts, account-based model |
| Monero | Ring signatures for enhanced privacy |
| Zcash | Zero-knowledge proofs for anonymous transactions |
| Cardano | Ouroboros proof-of-stake consensus |
Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology is being explored for various other applications, including:
- Supply chain management
- Digital identity verification
- Voting systems
- Decentralized finance (DeFi)
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs)
In each of these applications, cryptography plays a crucial role in ensuring security, privacy, and trust in a decentralized system.
However, it’s essential to note that while blockchain technology offers numerous advantages, it also faces several challenges. The rise of quantum computing, for instance, poses a potential threat to the cryptographic foundations of current blockchain systems. As a result, researchers are actively working on quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms to ensure the long-term security of blockchain technology.
As we’ve seen, cryptography forms the bedrock of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies, enabling a new paradigm of trustless, decentralized systems. These innovations are not only revolutionizing finance but also paving the way for new applications across various industries. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more sophisticated cryptographic techniques being developed and implemented in blockchain systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Cryptography is the art of data hiding and involves various methods of sending messages in a hidden form that only authorized recipients can decipher. The three types of Cryptography include Symmetric Key Cryptography, Asymmetric Key Cryptography, and Hash Functions. Each type has advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of type depends on the specific use case.
Cryptography stands as a cornerstone of modern digital security, offering powerful tools to protect our data and communications. From basic encryption techniques to advanced digital signatures, it plays a crucial role in safeguarding our increasingly connected world. As we’ve explored, cryptography’s applications extend far beyond just keeping secrets; it ensures the authenticity of digital transactions, secures our online identities, and even facilitates secure communication in an era of constant digital threats.
As technology evolves, so too does the field of cryptography. While cryptanalysts work tirelessly to break codes and expose vulnerabilities, cryptographers continue to develop more robust encryption methods. For individuals and organizations alike, implementing sound cryptographic practices in daily life is no longer optional—it’s a necessity. By understanding and applying these principles, we can all contribute to a safer digital ecosystem and protect our valuable information from prying eyes.
FAQs:
What is cryptography, and why is it necessary for data security?
Cryptography is the practice of encrypting and decrypting information to protect data confidentiality, integrity, and authentication. It’s essential for secure online transactions, private messaging, and safeguarding personal and corporate data against unauthorized access.
How does symmetric vs. asymmetric encryption work?
Symmetric encryption uses a single secret key for both encryption and decryption (e.g., AES), providing high performance for encrypting bulk data.
Asymmetric encryption (public-key cryptography, e.g., RSA, ECC) uses a pair of public and private keys to solve the key-distribution problem and enable digital signatures, at the cost of greater computational overhead.
What are the most common encryption algorithms used today?
The industry’s top algorithms include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) for symmetric encryption, RSA and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) for public-key operations, and SHA-256 for secure hashing. These standards strike a balance between strong security and proven performance.
How can I implement strong cryptography in everyday applications?
- Use TLS/HTTPS for all web traffic.
- Enable end-to-end encryption in messaging apps like Signal and WhatsApp.
- Store passwords as salted hashes (e.g., bcrypt, Argon2).
- Leverage multi-factor authentication and reputable key-management services.
Will quantum computers break today’s encryption?
Quantum algorithms like Shor’s threaten RSA and ECC by efficiently factoring large numbers. To future-proof your systems, adopt post-quantum cryptography (lattice-based or hash-based algorithms) as they become standardized.